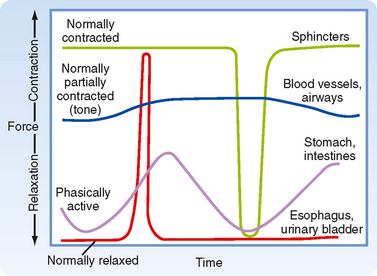
PLOS ONE: Abnormal Ca2+ Spark/STOC Coupling in Cerebral Artery Smooth Muscle Cells of Obese Type 2 Diabetic Mice

HuR (Human Antigen R) Regulates the Contraction of Vascular Smooth Muscle and Maintains Blood Pressure | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology
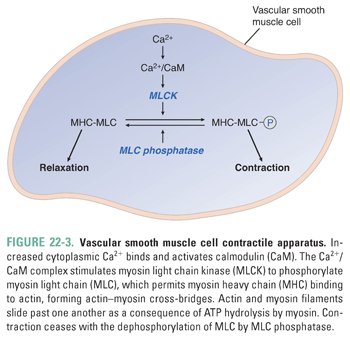
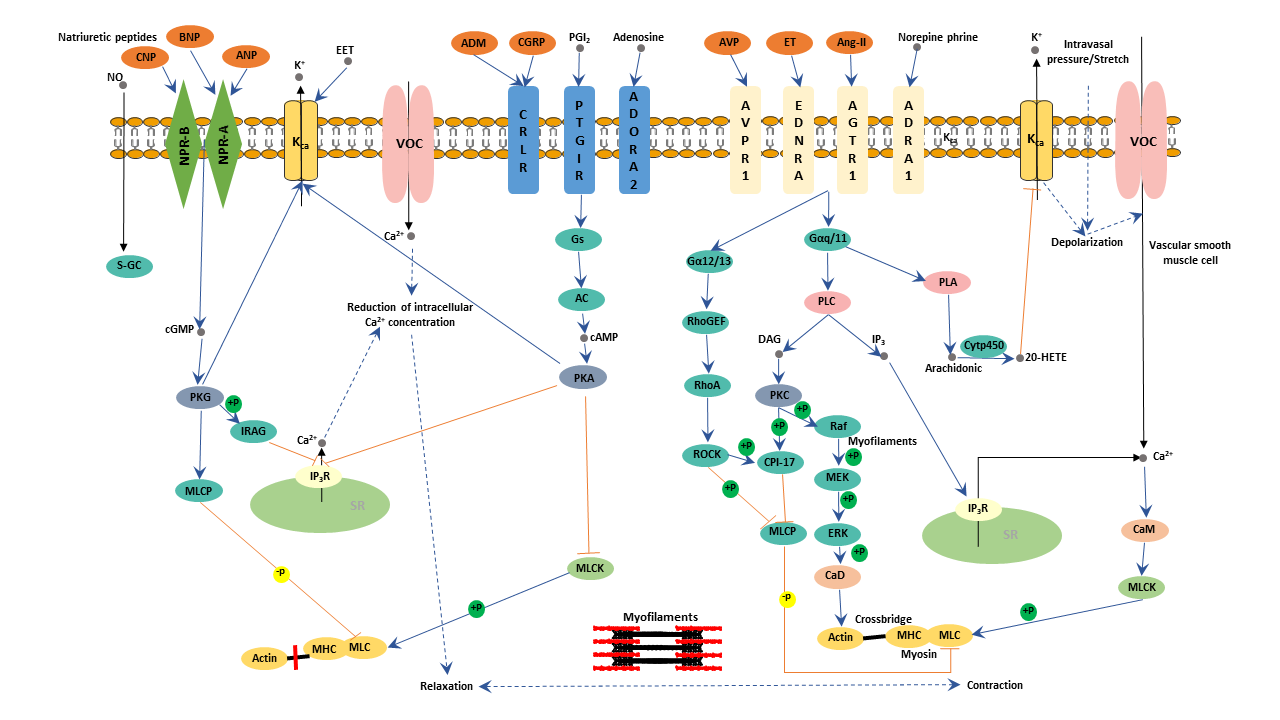
![PDF] Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders | Semantic Scholar PDF] Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8ee8ea0f1e1a9ab42fe163c73877b1865206909e/37-Figure10-1.png)
PDF] Mechanisms of Vascular Smooth Muscle Contraction and the Basis for Pharmacologic Treatment of Smooth Muscle Disorders | Semantic Scholar
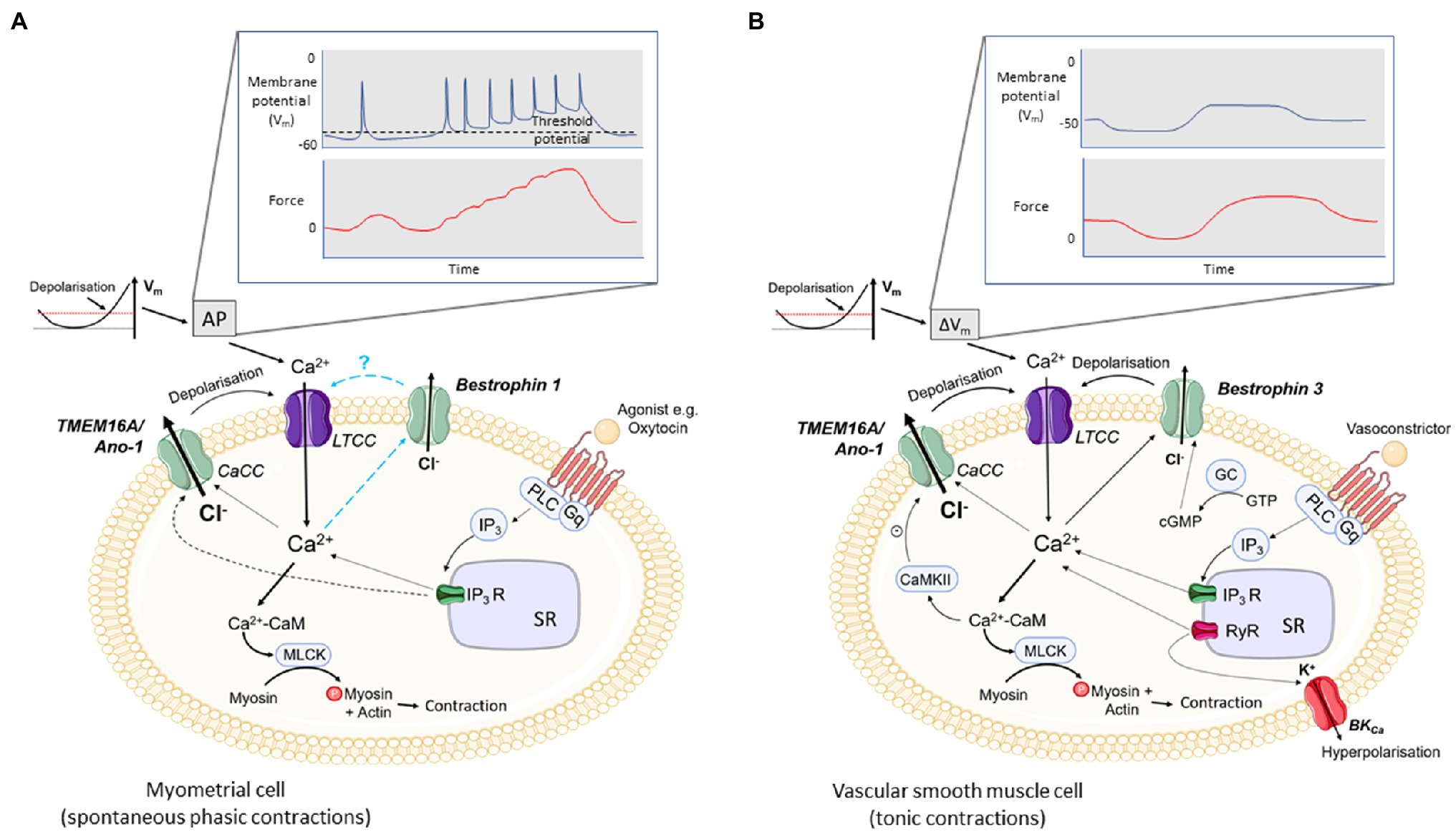
Frontiers | Calcium-Activated Chloride Channels in Myometrial and Vascular Smooth Muscle | Physiology

Regulation of vascular tone by nitric oxide (NO). NO regulates vascular... | Download Scientific Diagram

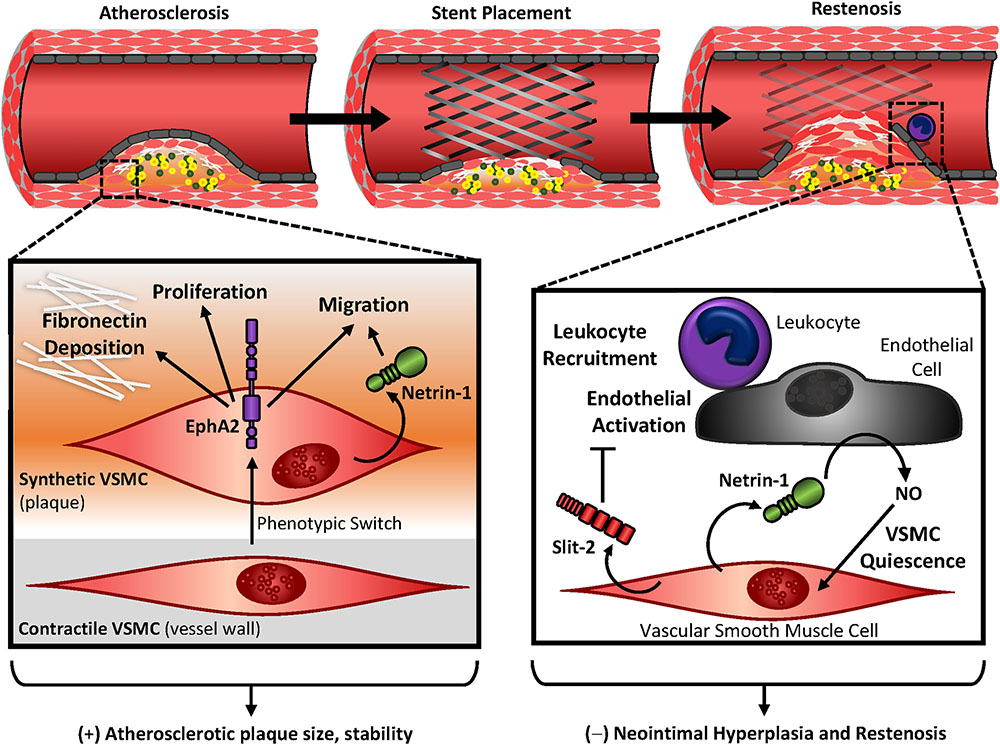
Not all vascular smooth muscle cell exosomes calcify equally in chronic kidney disease - Kidney International